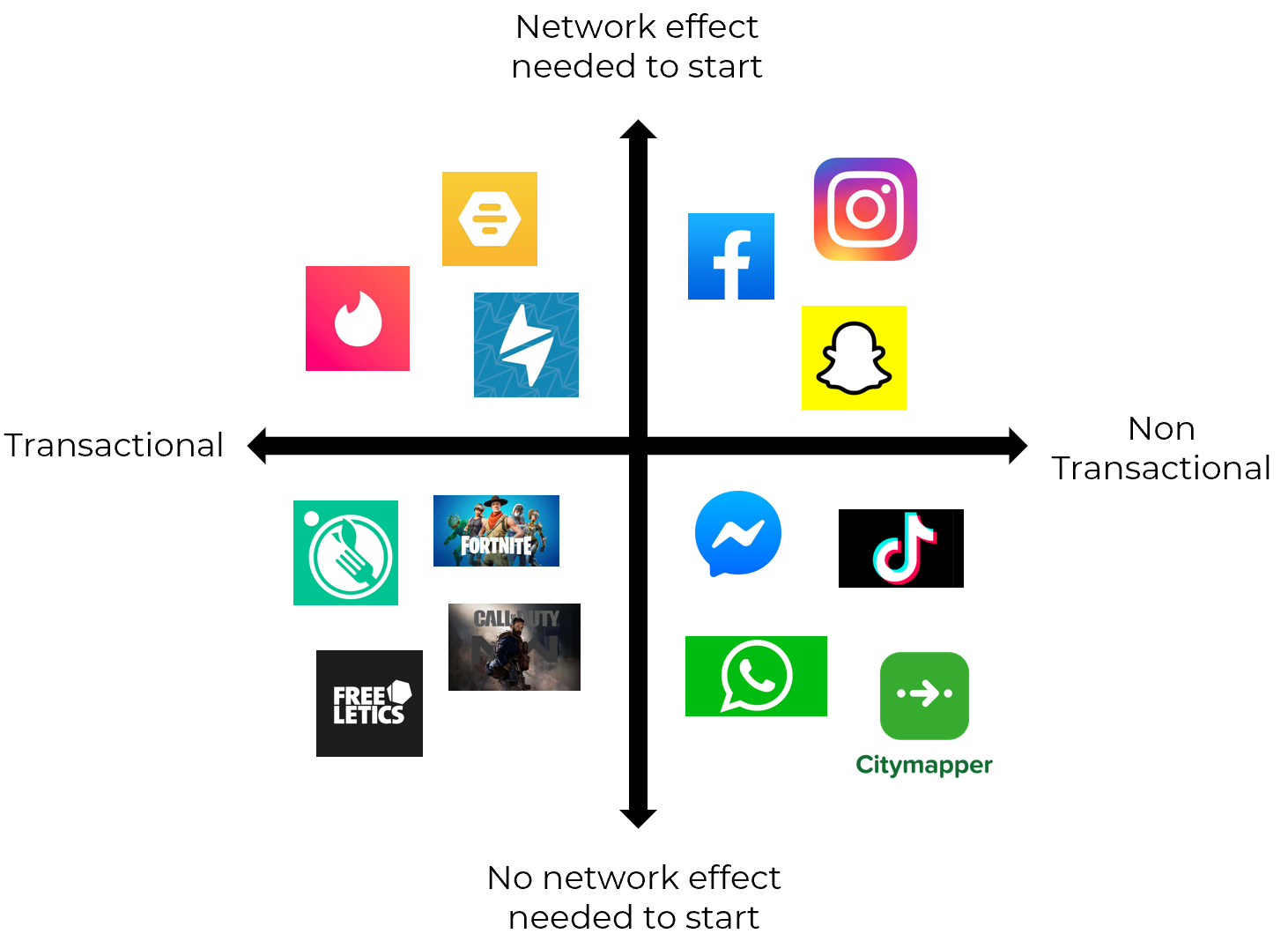
Non Location Based Dating Apps
This timeline of online dating services also includes broader events related to technology-assisted dating (not just online dating). Where there are similar services, only major ones or 'the first of its kind' are listed.
A location-based dating service, Happn shows you the profiles of other Happn users you've crossed paths with, along with time and location. This free dating app is one of the largest and most. Best Dating App for Non-Location based Dating? Posted by 4 minutes ago. Best Dating App for Non-Location based Dating? What dating apps let you put in cities/zip codes to sway who you get to view/swipe? Ideally ones that don't. Mar 17, 2021 Find a real relationship for $0 on these non-corny free dating sites. Out new dating apps and feel a rush. Match Group app to utilize location-based emergency services via Noonlight. Your bog standard swipe and match dating app based on location which allows you to send text, voice, video messages and even doodles to matches. You can see the last time matches logged on and also who’s been rummaging around in your profile. Meet24 is a free dating app with no ads or banners.
| Year (month and date) | Event | Venue |
|---|---|---|
| 1959 | Happy Families Planning Services launches. Started by Jim Harvey and Phil Fialer as a class project at Stanford. Used a questionnaire and an IBM 650 to match 49 men and 49 women. | |
| 1963 | Ed Lewis at Iowa State University uses a questionnaire and an IBM computer 'to optimize the meeting potential at dances'.[1] | |
| 1964 | St. James Computer Dating Service (later to become Com-Pat) launches. Joan Ball started the first commercially run computer generated matchmaking company. The first set of matchups was run in 1964.[2] | |
| 1965 | Operation Match (part of Compatibility Research Inc.) launches. Started by Jeff Tarr and Vaughan Morrill at Harvard. Used a questionnaire and an IBM 1401 to match students. There was a $3 fee for submitting a questionnaire. 'By the fall of sixty-five, six months after the launch, some ninety thousand Operation Match questionnaires had been received, amounting to $270,000 in gross profits, about $1.8 million in [2014]'s dollars.'[1] In the 1960s there still was no stigma about computer-assisted matching. | |
| 1965 | Eros (Contact Inc.) launches. Started by David Dewan at MIT. Used a dating questionnaire and Honeywell 200. 'In one distribution of questionnaires, he drew eleven thousand responses at $4 each, or $44,000 in gross profits, about $250,000 in [2014]'s dollars.'[1] | |
| 1965 | The New York Review of Books personals column makes a comeback. Slater writes:
| Magazine |
| 1968 | Data-Mate launches. Questionnaire-based matching service started at MIT.[3] | |
| 1970s, early | Phase II is founded. A 'computer-dating company' started by James Schur.[1] | |
| 1974 | Cherry Blossoms' mail-order bride catalog launches. Slater calls Cherry Blossoms 'one of the oldest mail-order bride agencies'. Started by John Broussard. | |
| 1976 | Great Expectations is founded. Video dating service started by Jeffrey Ullman.[4][5] The service achieved some notability, but it never overcame stigma. There were also apparently other video dating services like Teledate and Introvision, but it's nearly impossible to find anything about them online. | |
| 1980s | messageries roses (pink chat rooms) launches chat rooms for dating (using the Minitel network) started by Marc Simoncini. France. | |
| 1986[6] | Matchmaker Electronic Pen-Pal Network launches. A bulletin board system for romance started by Jon Boede and Scott Smith. Matchmaker grew to 14 local BBSs throughout the US. Eventually people lost interest as BBSs lost out to the World Wide Web, and Matchmaker was superseded by Matchmaker.com. | |
| 1987 | TelePersonals is created as a separate telephone dating system in Toronto, Canada from an earlier 'Personals' dating section of a telephone classified business. As part of an advertising program a selection of ads appear on the back pages of Now Magazine, the Canadian equivalent of the Village Voice. Services in different cities around the Toronto area are launched. A gay option is quickly added. The gay section becomes its own branded service. At the very beginning of the 2000s TelePersonals launches online and is rebranded as Lava Life with sections for cities across the United States and Canada. | Telephone, later Web |
| 1989 | Scanna International launches. Mail-order bride service focusing on Russia and Eastern Europe. | |
| 1994 | Kiss.com launches. The first modern dating website. | |
| 1995 | Yid.com launched as the first Jewish dating service and the first dating site in South Africa | Web |
| 1995 | Match.com launches. Started by Gary Kremen. | |
| 1997 | JDate launches dating service targeted at Jewish singles | |
| 1997 | Shaadi.com launches. It is an online wedding service founded by Anupam Mittal in 1997. October 1998, Sanjeev Bikhchandani, founder and executive vice chairman of Info Edge India, started the matrimonial website | |
| 1998 | Jeevansathi.com launches. October 1998, Sanjeev Bikhchandani, founder and executive vice chairman of Info Edge India, started the matrimonial website. | |
| 1999 | Gaydar launches. Founded in November 1999 by London-based South Africans Gary Frisch and his partner Henry Badenhorst, the website was once the world's most popular gay online dating site it grew into a portfolio of websites and an award-winning radio station. | Web later App |
| 2000 | eHarmony launches. Online dating service for long-term relationships. | |
| 2000 | BharatMatrimony launches. Murugavel Janakiraman started the BharatMatrimony website in 2000[7] while working as a software consultant for Lucent Technologies in Edison, N.J. In the late 1990s he set up a Tamil community web portal, which included matrimonial ads. He started BharatMatrimony after noticing the matrimonial ads generated most of his web traffic | |
| 2001 | Christian Mingle launches dating service for Christian singles | |
| 2002 | Friendster is launched. A friendship, dating and early general Social networking website all rolled into one. In 2005 Facebook copies and expands the idea into a general social interconnected website. | Web |
| 2002 | PlanetRomeo is launched as GayRomeo in October 2002 initially only available in German but now available in 6 languages. The majority of the sites users are based in Europe. | Web later App |
| 2002 | Dudesnude is launched as a networking site for gay men. The company slogan is 'picture, video, and profile sharing for men!' | Web |
| 2002 | Ashley Madison is launched as a networking service for extramarital relationships. | |
| 2002 | PrimeSingles.net launches as a dating service for singles over 50. This name changes to Single Seniors Meet in 2009 and to SilverSingles in 2011 | |
| 2003 | Proxidating launches. Dating service that used Bluetooth to 'alert users when a person with a matching profile was within fifty feet'.[1] | |
| 2003 | PlentyOfFish launches. | Web |
| 2004 | OkCupid launches. | Web |
| 2006 | Spark Networks, owner of niche dating sites like Jdate and Christian Mingle, goes public.[7] | |
| 2006 | Badoo launches as a dating-focused social networking service | |
| 2006 | SeekingArrangement launches. A sugar daddy/sugar baby site in the US. | |
| 2007 | Skout launches. A 'location-based social networking and dating application and website'. | |
| 2007 | Crazy Blind Date launches. Blind dating service started by Sam Yagan. | |
| 2007 | Zoosk launches. A global online-dating service started by Shayan Zadeh and Alex Mehr. | |
| 2008 | GenePartner launches matching service based on 'DNA compatibility'.[8] | |
| 2009 | Grindr launches, focussing on gay, bi and trans people. | App |
| 2010 | Scruff launches, focussing on gay, bisexual, and transgender men, adding in 2013 a HIV-positive community. | App |
| 2011 | LikeBright launches. Online dating site by Nick Soman.[9] By 2014 the site shut down.[10] | Web |
| 2011 | Dating group Spark Networks acquires Senior Singles Meet (formerly PrimeSingles) and changes the name to SilverSingles | |
| 2011 (July) | Momo, a Chinese social search and instant messaging app launches. | |
| 2011 (September) | Blendr, designed to connect like-minded people, launches. | |
| 2012(?) | Highlight launches. Slater calls it a 'location-based dating app'. | App |
| 2012 | Tinder launches. | App |
| 2012 | Hinge launches, an app 'designed to be deleted' | App |
| 2014 (Passover) | JSwipe launches. A dating app for Jewish millennials. | App |
| 2014 | Bristlr launches, facilitating communication between bearded men and women who love beards. | |
| 2014 (July) | 3nder starts facilitating communication between people interested in polyamory, kink, swinging, and other alternative sexual preferences. | |
| 2014 (September) | Spoonr starts facilitating communication between strangers who live within walking distance from each other. | |
| 2014 (December) | Bumble launches, a location-based mobile app that permits only women to start a chat with their matches.[11] | |
| 2015 | Personal information of Ashley Madison users stolen and released. | |
| 2015 | Huggle starts connecting users based on commonality of places they frequent. | |
| 2015 | Yellow, a Tinder for teens, launches in France and in 2017 in the US. | |
| 2015 | Jdate owners Spark Networks Inc buy JSwipe from Smooch Labs.[12] | |
| 2015 (November 19) | Match Group, which owns and operates several online dating web sites including OkCupid, Tinder, PlentyOfFish, and Match.com, goes public. | |
| 2017 | Affinitas GmbH (owner of dating websites like EliteSingles and eDarling) merges with Spark Networks, Inc, (owner of dating websites like Christian Mingle, Jdate, and SilverSingles) to create Spark Networks SE | |
| 2019 | Spark Networks SE acquires Zoosk, forming North America's second-largest dating company in revenues.[13] | |
| 2020 | Spark dating app launches in Canada with a focus on creative matchmaking[14] | App |
| 2021 | Beyond Dating app launches in India focusing on Interest matching, Profile Shorting Mode, and a unique Barrier. The Barrier is a personal matching test to get matched with the desired person. | App |
Proximity Based Dating App
Dominance of online dating[edit]
A 2017 survey tracked the change in how Americans meet their spouses and romantic partners since 1940. The results showed a steep increase in the proportion of couples whose first interaction occurred through online media.[15][16]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ abcdefSlater, Dan. A Million First Dates.
- ^Hicks, Marie (2016). 'Computer Love: Replicating Social Order Through Early Computer Dating Systems'. Ada: A Jornal of Gender, New Media and Technology. ISSN2325-0496.
- ^Lawrence Krakauer writes about his experiences here.
- ^Ullman, Jeff. 'Jeff Ullman'. LinkedIn. Retrieved December 4, 2016.
Great Expectations (video dating) December 1975 – January 1997 (21 years 2 months) Created, served as CEO, and primary international media spokesperson for 'Great Expectations', which we built into the world's largest introduction service for singles (aka, 'video dating').
- ^Wallace, Amy (January 16, 1994). 'Love God From Hell : The Man Who Brought You Videodating Hates to Date, Loves to Taunt and Has Himself Been Unlucky in Love. Would You Buy a Relationship From Jeffrey Ullman?'. Los Angeles Times. Retrieved December 4, 2016. Dan Slater references this article.
- ^Slater, Dan.
- ^Gelsi, Steve. 'Spark Networks files $75 million IPO'. MarketWatch. Retrieved 2019-11-20.
- ^Arrington, Michael (July 22, 2008). 'Ok, We Have Our First DNA-Based Dating Service: GenePartner'. TechCrunch. Retrieved December 4, 2016.
- ^Soper, Taylor (December 20, 2013). 'Matchmaking platform LikeBright raising $1M to help singles land a 2nd date'. GeekWire. Retrieved December 4, 2016.
- ^Soper, Taylor (September 18, 2014). 'Matchmaking platform LikeBright morphs into Reveal, a new anonymous chat app'. GeekWire. Retrieved December 4, 2016.
- ^'Bumble is a dating app where women take lead'. Thestar. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^'JDate Bought JSwipe and Everyone Loves Each Other Now'. Observer. 2015-10-15. Retrieved 2019-11-20.
- ^'Spark Networks SE Closes Zoosk, Inc. Acquisition'. finance.yahoo.com. Retrieved 2019-11-20.
- ^'Spark Networks Launches 'Creativity-Focused' Dating App 'Spark''. Global Dating Insights. 2020-06-25. Retrieved 2021-01-22.
- ^'How Couples Meet and Stay Together SSDS Social Science Data Collection'. data.stanford.edu. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
- ^'How Couples Meet and Stay Together 2017 (HCMST2017) SSDS Social Science Data Collection'. data.stanford.edu. Retrieved 2019-12-07.
A number of location-based dating apps can be used to track the real-time locations of users, armed with nothing more than their username and the official API…
The problem was discovered by researchers from security firm Pen Test Partners (PTP), who were able to find out where users live, work, and socialize.
We were able to precisely locate and track the users of four major dating apps, potentially putting at risk 10 million users […]
Many of these apps return an ordered list of profiles, often with distances in the app UI itself. By supplying spoofed locations (latitude and longitude) it is possible to retrieve the distances to these profiles from multiple points, and then triangulate […] the data to return the precise location of that person.
We created a tool to do this that brings together multiple apps into one view. With this tool, we can find the location of users of Grindr, Romeo, Recon and 3fun – together this amounts to nearly 10 million users globally […]
The location data collected and stored by these apps is also very precise – 8 decimal places of latitude/longitude in some cases […] In our testing, this data was sufficient to show us using these data apps at one end of the office versus the other.
The company illustrated this by tracking app users in sensitive locations in London. This included someone who appears to be in 10 Downing Street, home to the Prime Minister of the UK, as well as in the British parliament and other government buildings. PTP redacted the usernames of these users.
This vulnerability not only exposes people to the danger of being stalked, but could also carry other risks for members of some communities.
In the UK, members of the BDSM community have lost their jobs if they happen to work in “sensitive” professions like being doctors, teachers, or social workers. Being outed as a member of the LGBT+ community could also lead to you using your job in one of many states in the USA that have no employment protection for employees’ sexuality.
Location Based Services
But being able to identify the physical location of LGBT+ people in countries with poor human rights records carries a high risk of arrest, detention, or even execution. We were able to locate the users of these apps in Saudi Arabia for example, a country that still carries the death penalty for being LGBT+.

Two of the app makers responded positively, the other two not.
Romeo replied within a week and said that they have a feature that allows you to move yourself to a nearby position rather than your GPS fix. This is not a default setting and has to be found enabled by digging deep into the app.
Recon replied with a good response after 12 days. They said that they intended to address the issue “soon” by reducing the precision of location data and using “snap to grid”. Recon said they fixed the issue this week.
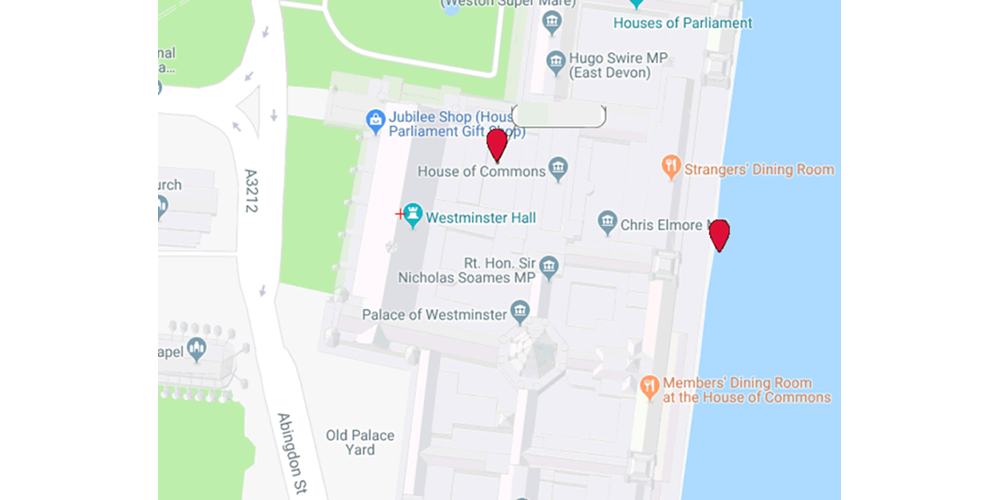
3fun’s was a train wreck: Group sex app leaks locations, pics and personal details. Identifies users in White House and Supreme Court
Grindr didn’t respond at all. They have previously said that your location is not stored “precisely” and is more akin to a “square on an atlas”. We didn’t find this at all – Grindr location data was able to pinpoint our test accounts down to a house or building, i.e. exactly where we were at that time.
PTP is calling on developers of location-based dating apps to protect user privacy by collecting less precise location data, use a snap-to-grid approach and inform users of the risks, allowing them to choose to identify their location in more general terms. It also suggests that Apple and Google could offer less precise location APIs for use by dating apps.
Non Location Based Dating Apps For Women
A recent study suggested that dating apps and websites are now the most common way for couples to meet.
FTC: We use income earning auto affiliate links.More.